GENERAL
Waste Management and Sustainability in Reducing Waste
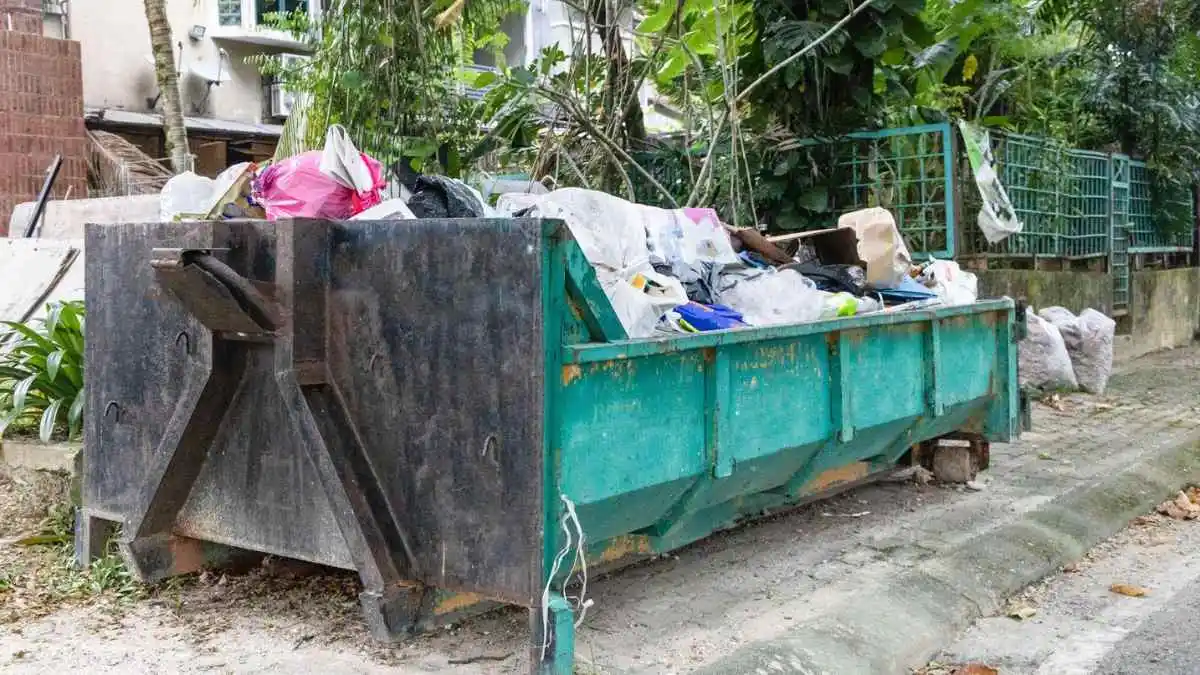

Waste management is a critical aspect of modern society, ensuring that waste is collected, processed, and disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner.
With global waste production increasing at an alarming rate, implementing efficient waste management strategies is essential to reduce pollution, conserve natural resources, and promote sustainability.
What’s more, waste management practices seek to find ways of managing waste that are both efficient and environmentally friendly.
This blog explores the waste management hierarchy, its benefits, and the challenges associated with proper waste disposal.
Understanding Waste Management
Waste management is the practice of collecting, moving, treating, discarding, recycling, or reusing material from a previous resource with the intention to reduce the damage done to the environment and society during those processes.
It includes processes such as repairing or replacing broken pieces of equipment, using energy or resources for composting, and increasing available space in landfills to lower pollution levels.
Waste management solutions commonly seek to promote recycling materials, waste sorting, and other waste management processes.
Additionally, waste services are capable of dealing with food waste, organic waste, hazardous waste, liquid waste, garden waste, and general business waste.
The Waste Management Hierarchy
In regards to assessing the level of development of a society, hierarchical frameworks are one of the many ways to distinguish the systematic ordering of social needs.
This emphasises constructing truthful information on ignoring declining waste productivity while raising efficiency in the use of extracted resources.
The hierarchy goes in six sequences from the top that are most preferred, to the least.
Prevention
Products and techniques should be developed with the intent to create less waste. This results in fewer follow-up steps needed in managing waste.
Waste Minimisation
Waste Minimisation concentrates on eliminating, to the greatest extent possible, the waste produced during creation and consumption processes. Adopting more efficient production practices and promoting mindful consumption can dramatically prevent waste creation.
Waste Reuse
Reusing includes looking for ways to use products or parts of products that would otherwise be thrown away. Through innovative reuse strategies, we can delay the need for new resources by lengthening the life of many items.
Waste Recycling
Recycling is the process of reclaiming waste to produce new materials in order to conserve the earth’s materials and minimise pollution. Commonly recycled items include paper, plastics, metals, and electronic devices.
Waste Recovery
Some waste that cannot be recycled can be converted into usable energy, such as heat, electricity, or fuel. Waste can be incinerated and energy captured, which reduces waste volume and generates energy.
Waste Disposal
Disposal is the option that is the least favoured when dealing with waste. The treatment and placing of waste onto the ground that cannot be managed in any other way is referred to as landfilling. This option has its place, but it is essential to avoid these activities as much as possible because of their harmful effects on the environment.
Developing allocative efficiency helps individuals and organisations focus on actions needed to promote sustainable resource management and balance conservation, prevention, and restoration. Placing prevention and reduction as a priority helps achieve waste management in an efficient and effective manner.
Benefits of Effective Waste Management
The benefits of effective waste management typically go beyond the standard better disposal of waste materials. In reality, good waste management can also be good general business practices.
Additionally, protecting the environment can be done alongside saving costs. This makes it very effective for any small business or household.
Environmental Protection
Appropriate waste management activities also aid in the prevention of pollution, conservation of biodiversity and their habitats, as well as mitigating climate change owing to waste and hazardous material management towards landfills and incinerators.
Resource Conservation
Reducing waste also helps save some natural resources which are limited and in excess would require environmental destruction, whereby less raw materials are needed, consequently reserving the greater part of the environment.
Energy Production
With the advancement of technology, waste-to-energy processes provide renewable sources of energy for purposes and reduce the dependency on fossil fuels.
Economic Growth
There are numerous job opportunities in the waste management industry with the collection, sorting, recycling, composting, and treatment of waste, thus leading to economic development and progress in industries.
Public Health Improvement
Proper and efficient management of waste helps in preventing a wide range of disease outbreaks due to exposure to hazardous waste and the general living environment being cleaner.
Challenges in Waste Management
Like any industry, there are challenges within the waste management services available. These are commonly related to the way that waste is managed in order to safeguard human health and the environmental impacts.
Generally, waste management systems work well, but it is equally important to understand their challenges before implementing any of their solutions.
High Operational Costs
A region may be unable to put forth efficient waste solutions since there is a great expense related to constructing and maintaining the infrastructure.
Lack of Public Awareness
Appropriate disposal methods are not adhered to by a number of people and organisations due to improper education regarding waste management which in turn worsens the environmental crisis.
Inconsistent Regulations
Sustainability goals are difficult to achieve because waste management policies in certain regions do not align with other goals like enforcing stronger environmental policies.
Limited Recycling Facilities
Waste processing needs to be done in a certain way, and if the means are not present, then important elements will be thrown away instead of reused.
Illegal Dumping and Pollution
Waste that is unattended to greatly fuels the pollution of land and water, damaging wildlife. This also opposes the effort to manage waste sustainably.
Conclusion
To deter resources and habitats from suffering, managing waste efficiently is a core part needed. Lessening waste treatment is essential in ensuring a better and cleaner future. This brings forth the means for businesses and even the general public to put effort into not only dealing with, but also preventing the waste crisis.
-

 BIOGRAPHY9 months ago
BIOGRAPHY9 months agoBehind the Scenes with Sandra Orlow: An Exclusive Interview
-

 HOME1 year ago
HOME1 year agoDiscovering Insights: A Deep Dive into the //vital-mag.net blog
-

 HOME2 years ago
HOME2 years agoSifangds in Action: Real-Life Applications and Success Stories
-

 BIOGRAPHY1 year ago
BIOGRAPHY1 year agoThe Woman Behind the Comedian: Meet Andrew Santino Wife