HEALTH AND FITNESS
How EDI Supports HIPAA-Compliant Healthcare Transactions?

Introduction
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) transformed healthcare by allowing providers, payers, pharmacies, and clearinghouses to exchange administrative and clinical data in standardised digital formats. From claims to eligibility requests, remittances, and enrollments, EDI replaces labour-intensive procedures, paper forms, fax machines, and phone calls by exchanging streamlined, error-free communications between disparate systems.
With the increasing dependence of healthcare on digital transactions, HIPAA-Compliant EDI in Healthcare ensures the security, privacy, and integrity of Electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI). This blog discusses what HIPAA-Compliant EDI in Healthcare is, how EDI complies with it, and why a safe EDI environment is essential for healthcare in the contemporary era.
What is HIPAA and Why Compliance Matters
What Is HIPAA?
According to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which was enacted in 1996 in the United States, protecting protected health information (PHI) in verbal, physical, or electronic formats is regulated. Even though it was designed with the United States in mind, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) has become a model that is followed worldwide, notably by businesses that work with corporations based in the United States.
Key HIPAA Standards
HIPAA-Compliant EDI in Healthcare has three main rules:
Privacy Rule: Specifies what uses and disclosures of PHI are permitted, including patients’ rights of access to their records.
Security Rule: Mandates that ePHI be safeguarded through administrative, physical, and technical safeguards like encryption, access controls, and secure backups.
Transaction and Code Set Standards: Establishes common EDI standards in healthcare, such as ANSI X12 (837, 835, 270/271) for administrative transactions.
Why Compliance Cannot Be Ignored
HIPAA compliance in healthcare (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is not optional but necessary. Not being HIPAA-compliant EDI in Healthcare can seriously affect your finances, reputation, and legal standing. Civil penalties can be as low as a few thousand dollars to as much as $1.5 million per year per infraction category, depending on how serious and what kind of violation it is. Along with these fines, businesses may also have to deal with litigation, government investigations, and damage to their brand that lasts for a long time. Non-compliance with HIPAA can have the following consequences:
- Heavy legal penalties (up to $1.5 million per year per violation category)
- Civil penalties and negative reputation
- Loss of business trust with business partners and patients
- Organisations that comply with HIPAA sidestep these risks while establishing a cornerstone of trust and credibility.
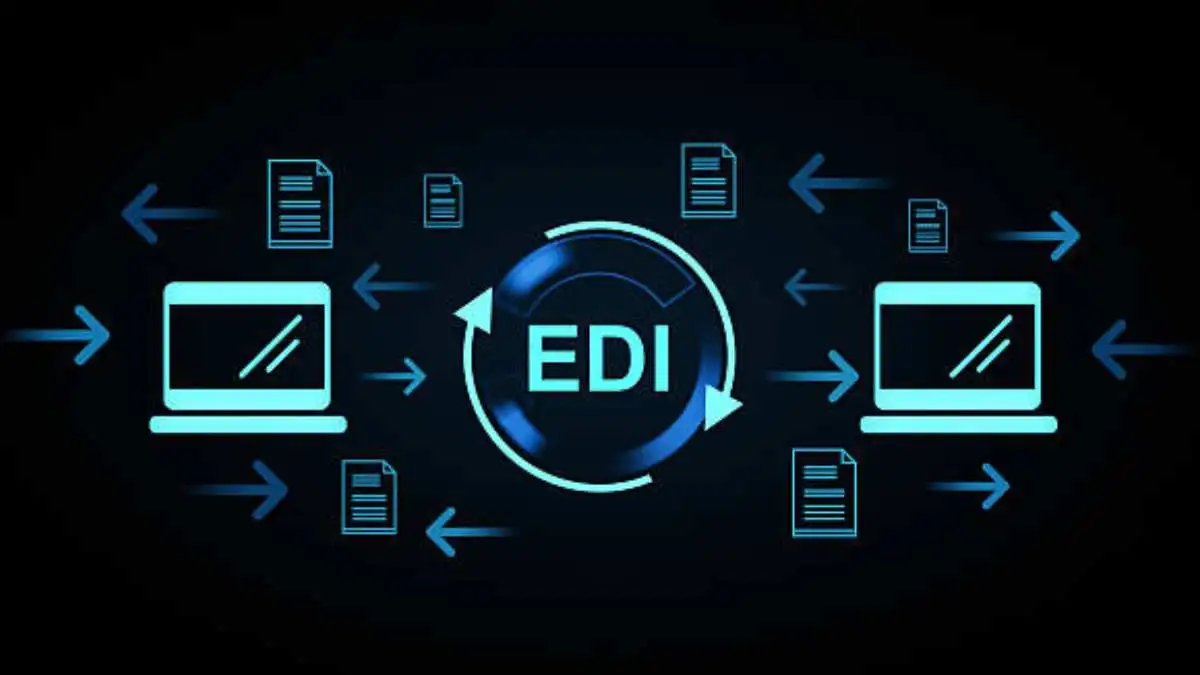
Understanding EDI in Healthcare
Defining EDI in Healthcare
HIPAA-Compliant EDI in Healthcare streamlines the transfer of structured, standardised data between systems. With the use of formats such as ANSI X12 or NCPDP, EDI facilitates rule-based, automated processing, rapidly transferring information from systems like EHRs, ERPs, and bill systems without the intervention of human handlers.
Popular Healthcare EDI Transactions Sets
The most important HIPAA-compliant EDI formats are:
- 837 – Claims submission
- 835 – Remittance advice
- 270/271 – Eligibility inquiry and response
- 834 – Enrollment and benefit maintenance
- 276/277 – Inquiry and response for claim status
- NCPDP – Pharmacy retail claims
These EDI standards in healthcare map to normal administrative workflows, providing operational consistency and machine-readability.
How EDI Automates Process
By automating administrative processes, EDI facilitates:
- Claims Submission (837) – Electronic claim generation and instant submission to payers
- Eligibility Checks (270/271) – Instant patient coverage verification before treatment
- Remittance Advice (835) – Payer replies with extended payment dispositions
- Enrollment Management (834) – Secure updating of benefit plan participation
- Prior Authorisation (278) and Claim Status Updates (276/277) – Quick decisions and status monitoring
This automation eliminates manual errors, processing time, and operating expense.
How EDI Facilitates HIPAA Compliance
EDI Standards Compliant with HIPAA
HIPAA requires administrative transactions to comply with certain standards (for example, ANSI X12 for claims eligibility). The standard formats used by EDI enforce these precise requirements, so there is compliance at the data-structure level. After correctly mapping, any EDI document automatically complies with HIPAA’s format standards.
Secure Data Exchange & Encryption
To be in line with HIPAA, it’s important to keep electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) safe while it’s being delivered and stored. Secure data exchange is the most important part of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in healthcare. It makes sure that sensitive patient information is never available to anyone who shouldn’t have it. A well-secured EDI system uses up-to-date encryption techniques and transmission standards to protect against data breaches, cyberattacks, and employee misuse.
HIPAA says that ePHI must be encrypted when it is being sent and when it is not being sent. Secure EDI systems usually use the following technologies to do this:
AS2 (Applicability Statement 2): Lets you securely send HTTP-based messages with encryption, and it supports digital signatures and message integrity.
SFTP and FTPS are secure file transfer protocols that let systems talk to each other over encrypted, authorised channels.
TLS (Transport Layer Security): Encrypts data and verifies endpoints to keep communications safe while they are being sent.
VPN Tunnels: Set up secret, encrypted network connections to ensure that communication across faraway networks is safe and regulated.
As HIPAA regulations require, these technologies work together to keep patient health data private, safe, and available.
Data Integrity & Audit Trails
Each EDI message is stamped with electronic timestamps, sender/recipient information, and checksum verification. This enables:
- Proof of delivery and receipt acknowledgement
- Audit readiness for internal and regulatory audits
- Non-repudiation for safe business exchanges
Such traceability enhances HIPAA’s audit and accountability requirements.
Lower Errors & Privacy with Automation
Automating hands-off data handling automates the reduction of:
- Entry-based errors (typos, omissions)
- Lost paper forms or faxes
- Exposure to illegitimate access via insecure conduits
Structured EDI processes prevent accidental disclosure and enhance patient privacy.
Principal Benefits of HIPAA-Compliant EDI
Speedier Claims Processing & Payment Cycles
EDI allows claims to be processed and received in minutes instead of days. Accelerated adjudication speeds up reimbursements and enhances revenue cycles.
Improved Patient Data Protection
Authenticated, encrypted Healthcare EDI Transactions safeguard PHI from unauthorised viewing, audits, or breaches, maintaining patient confidence and institutional credibility.
Administrative Cost Savings & Reduced Administrative Burden
EDI minimises paper, mailing, and manual effort. Payers and providers reduce labour expenses and operational inefficiency.
Simplified Stakeholder Communication Standardised structures allow providers, payers, and clearinghouses to use identical information, enhancing coordination and decreasing errors.
Integrated Audit Trails & Reporting
Detailed logs facilitate HIPAA audits and internal governance, making identifying anomalies or compliance deficits simpler.
Scalability & Automation-Driven Productivity
EDI platforms can auto-scale to grow with expanding volumes of transactions and accommodate hybrid models, allowing staff to concentrate on caring for patients instead of filling out paperwork.
Challenges in Implementing HIPAA-Compliant EDI
Interoperability with Legacy Systems
Most healthcare organisations have legacy systems that were never written for current EDI requirements. Secure EDI integration takes custom mapping, middleware, API gateways, time, and money.
Setup and Training Fees
Protocol choice (AS2 vs. SFTP), adding encryption, and connecting with partners require vendor costs, internal code development, and speciality support. Instructor-led training for HIPAA/EDI processes adds to the out-of-pocket expense.
Remaining Compliant with Changing Regulations
HIPAA is changing simultaneously with encryption regulations and national privacy legislation. EDI environments need constant updating with patching, auditing, and certificate renewal, a serious task.
Staff & Partner Change Management
It may be challenging to transition trading partners and staff from paper/fax to secure EDI. Implementation demands formal change management, as well as ongoing communication.
Best Practices for HIPAA-Compliant EDI
Partner with Certified EDI Providers
Partner with suppliers of secure, HIPAA-compliant EDI Managed Services and healthcare-born platforms. They include mapping, encryption, and compliance built into the solution.
Perform Routine Security Testing
Perform annual vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and policy audits. Rotate encryption certificates and audit partner connections regularly.
Regular Staff Training
Train employees on PHI handling, secure messaging, login safety, and phishing training. Staff responsibilities should align with roles and permissions.
Ongoing Monitoring of TransactionsUtilisee security dashboards to identify anomalies, transmission failures, or unauthorised EDI access. Initiate alerts and workflows for swift incident response.
Maintain Documentation & Certification Up-to-Date
Upkeep policy documents, audit logs, business associate agreements, and training records. Remain current with any HIPAA, HITECH, or national privacy law changes.
Why Select A3Logics EDI Managed Services?
Proven Experience: A3Logics has expertise in healthcare-grade EDI, with multi-layered encryption, TLS connectivity, and secure audit trails compliant with HIPAA standards.
Seamless Integration: Our architecture integrates EDI with EHR, ERP, and CRM applications through data mapping, APIs, and secure middleware.
End-to-End Security: Each phase is safeguarded with ISO 27001-level security and encryption from mapping and transmission to storage.
Custom EDI 834 services: Our team of specialists offers custom benefits enrollment automation with smooth onboarding, updates, and reporting.
Flexible Infrastructure: We provide cloud-hosted, hybrid, or on-prem solutions featuring managed uptime, certificate refresh, version management, and partner onboarding.
Affordable Support: Our EDI managed services ensure you remain compliant, current, and secure without requiring an in-house big team.
Conclusion
Secure, HIPAA-compliant EDI in healthcare is the living infrastructure supporting modern, efficient, and reliable healthcare transactions. It guarantees:
- Encrypted and authenticated data exchanges
- Reduction of systematic error and auditability
- Accelerated claims, eligibility verifications, and remittances
- Decreased labour, enhanced compliance, and enhanced patient experience
By integrating with certified providers such as A3Logics and implementing best practices such as staff training, continuous risk assessment, and smooth system integration, healthcare organisations can reap the full benefits of secure EDI while complying with regulatory requirements. In today’s digital-first world, those solutions are necessary, not an option.
To learn more, visit our blog for the latest trends and technologies.
-

 BIOGRAPHY9 months ago
BIOGRAPHY9 months agoBehind the Scenes with Sandra Orlow: An Exclusive Interview
-

 HOME1 year ago
HOME1 year agoDiscovering Insights: A Deep Dive into the //vital-mag.net blog
-

 HOME1 year ago
HOME1 year agoSifangds in Action: Real-Life Applications and Success Stories
-

 BIOGRAPHY1 year ago
BIOGRAPHY1 year agoThe Woman Behind the Comedian: Meet Andrew Santino Wife