GENERAL
Discover Nahttypen: Seam Types for All Applications

Nahttypen is a German term that translates to “types of seams” and refers to the various methods used to join materials such as fabrics or tissues. In textiles, it encompasses seam types such as straight stitch, flat-felled, French, and overlock seams, chosen based on their durability, flexibility, and aesthetic appeal. In medical contexts, it relates to suturing techniques used to close wounds or surgical incisions. Each Nahttypen is selected according to the functional, structural, and visual requirements of the application.
Cultural Relevance of Nahttypen
In German-speaking countries, the term “Nahttypen” is a staple of both academic curricula and industry terminology. Students in tailoring, fashion design, and medical programs are trained extensively in the various seam types, ensuring mastery before they enter their respective professions.
Furthermore, with the global reach of German engineering and design principles, “Nahttypen” is increasingly referenced in international contexts, particularly in fashion manufacturing, technical garment construction, and surgical disciplines.
Nahttypen in Sewing and Garment Construction
Nahttypen play a major role in the determination of the way two or more pieces of cloth are stitched together in the textile industry.
1. Geradstichnaht (Straight Stitch Seam)
Another very common seam is the Geradstichnaht or straight stitch seam, which is very easy yet effective. It implies placing two pieces of fabric edge to edge and sewing them together using a straight line of stitch.
- Applications: Suitable for non-stretch materials, i.e., cotton, linen, and wool.
- Sequences Advantages: It is easy to perform, is quick to apply, and is very versatile.
- Disadvantages: It is not elastic, hence not applicable in stretch materials or areas where movement is high.
2. Kappnaht (Flat-Felled Seam)
The Kappnaht, which is sometimes called the flat-felled seam, is very common in wearable clothing like jeans and workwear. It is when one edge of a piece of fabric is turned under and sewn, forming a flat, doubled stitch.
- Uses: Usually found in denim clothing, outdoor apparel, and stress-prone places.
- Pros: High quality, well built, gives a professional feel both on the inside and outside.
- Disadvantages: A little bit more difficult to sew and may be clunky on lighter materials.
3. Französische Naht (French Seam)
The Französische Naht or French seam covers the unfinished edges of cloth on the inside of the seam, and, at the same time, turns into a practical and pretty seam. This type of seam applies in light clothes and light materials such as chiffon and silk.
- Usage: Lingerie, wedding gowns, casual blouses.
- Pros: Looks presentable and tidy, will not fray, works well with fragile materials.
- Disadvantages: Time-consuming stitch and ineffective when it comes to thick or bulky materials.
4. Overlocknaht (Overlock Seam)
The Overlocknaht or overlock seam is made with an overlock machine, and it trims, sews, as well as crimps the fabric edge at the same time. This is a type of seam that is very popular in mass production and modern stitching assignments.
- Uses: Knit, athletics, and casual clothing.
- Positives: Easy to use, does not fly, and it is easily applied.
- Disadvantages: It needs a special type of equipment and could be less powerful as flat-felled seams could be used as heavy-duty seams.
Functional and Aesthetic Considerations
When choosing a seam type, seamstresses and designers consider multiple factors:
- Durability: Flat-felled and overlock seams offer increased strength.
- Flexibility: Overlock seams are ideal for garments that require stretching.
- Aesthetics: French seams deliver a refined, invisible finish.
- Fabric Type: Lightweight fabrics benefit from enclosed seams, while heavier textiles demand reinforced seams.
Nahttypen in Medical Applications
In medical terminology, Nahttypen refers to various suture techniques used to close wounds or surgical incisions.
1. Einzelknopfnaht (Simple Interrupted Suture)
This technique involves individual stitches tied separately. It allows precise adjustment of tension in each stitch and offers a high level of control.
- Functionality: Precise tension control
- Applications: Facial wounds, hand surgeries
2. Fortlaufende Naht (Continuous Suture)
A continuous line of stitches is made without cutting the thread. It’s faster than interrupted sutures but slightly less secure if a part fails.
- Functionality: Speed and minimal tissue reaction
- Applications: Long surgical incisions, abdominal surgeries
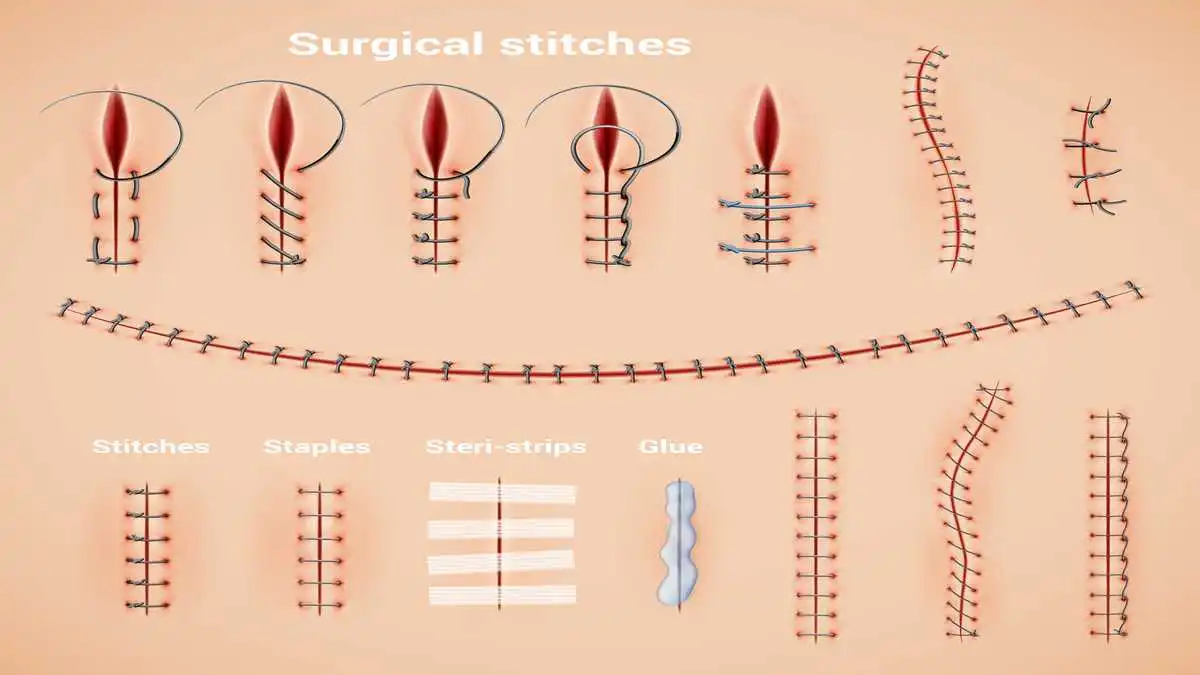
3. Intrakutane Naht (Subcuticular Suture)
Placed just under the skin surface, this suture is nearly invisible and used in cosmetic surgeries. It promotes minimal scarring and faster healing.
- Functionality: Aesthetic outcome
- Applications: Plastic surgery, dermatological procedures
4. Z-Nähte (Z-Sutures)
Z-sutures are used in cases where skin movement is a concern. They redistribute tension and help in wound closure without distorting surrounding tissues.
- Functionality: Tension distribution
- Applications: Joint areas, complex closures
Comparing Textile and Medical Nahttypen
| Feature | Textile Nahttypen | Medical Nahttypen |
| Purpose | Join fabric pieces | Close wounds/incisions |
| Tools Used | Sewing machine, needle, thread | Surgical needle, suture thread |
| Materials | Cotton, polyester, silk | Absorbable/non-absorbable sutures |
| Design Consideration | Durability, flexibility, aesthetics | Healing rate, scar minimization, tension |
| Common Types | Straight, French, Flat-felled, Overlock | Interrupted, Continuous, Subcuticular |
Modern Innovations and Technologies
The innovations in textile and medical filed have completely changed how Nahttypen are utilized and innovated. Wearable electronics Smart seams now include sensors and conductive threads in textiles. There are also methods of seamless knitting and bonding, which would eliminate the shaping.
Bioresorbable sutures, antibacterial coatings, and stitching with the help of robots are transforming how wounds are closed and healed in the medical world. The realm of seam types is no longer an issue of connecting two surfaces, but it is into a large system of efficiency, safety, and innovation.
Conclusion
Nahttypen unites old artisanship with high-precision modern technologies. Whether you are making an outfit that is going to runways or sealing the hole in an operating room, knowing the appropriate seam is the key to functionality, aesthetics, and security. Ranging in types, seeding the simplicity of Geradstichnaht to the intricacy of medical stitching in intracutaneous medical stitches, half theories work in their fields.
-

 BIOGRAPHY9 months ago
BIOGRAPHY9 months agoBehind the Scenes with Sandra Orlow: An Exclusive Interview
-

 HOME1 year ago
HOME1 year agoDiscovering Insights: A Deep Dive into the //vital-mag.net blog
-

 HOME1 year ago
HOME1 year agoSifangds in Action: Real-Life Applications and Success Stories
-

 BIOGRAPHY1 year ago
BIOGRAPHY1 year agoThe Woman Behind the Comedian: Meet Andrew Santino Wife